In the dynamic and ever-evolving landscape of the oil and gas industry, depth conversion seismic data has emerged as a foundational tool, providing invaluable insights into the Earth’s subsurface. Recent years have witnessed groundbreaking developments in the acquisition, processing, and interpretation of seismic data, revolutionizing exploration practices and unlocking new frontiers for the energy sector.
High-Resolution 3D Seismic Imaging
One of the significant developments in seismic data is the widespread adoption of high-resolution 3D seismic imaging. This technology allows for a more detailed and comprehensive view of subsurface structures. With the ability to capture intricate geological features, 3D seismic data enhances the accuracy of reservoir characterization and facilitates more precise well placement.
Broadband Seismic Technology
The advent of broadband seismic technology represents a leap forward in data quality and frequency range. Unlike conventional seismic sensors, broadband sensors can capture a broader spectrum of frequencies, providing a more detailed and nuanced representation of subsurface formations. This advancement is particularly beneficial in imaging complex geological structures and improving the overall resolution of seismic data.
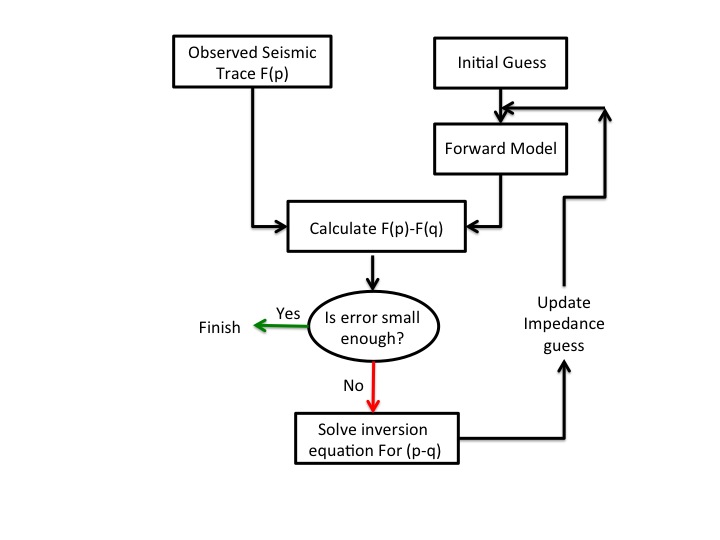
Full-Waveform Inversion (FWI)
Full-Waveform Inversion (FWI) is a sophisticated computational technique that has gained prominence in seismic data processing. FWI uses the entire seismic waveform to iteratively update the subsurface model, resulting in highly accurate and detailed images of the Earth’s subsurface. This technology enables geoscientists to achieve higher-resolution images and better characterize reservoir properties.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in a new era in seismic data interpretation. Advanced algorithms can analyse vast datasets with unprecedented speed and accuracy, identifying subtle patterns and anomalies that may elude traditional methods. Machine learning applications contribute to faster and more efficient seismic processing, enhancing the overall exploration workflow.
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS)
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) is a revolutionary technology that transforms conventional fibre-optic cables into seismic sensors. This allows for continuous and real-time monitoring of subsurface activities, offering a wealth of information about reservoir dynamics and fluid movements. DAS technology enhances reservoir management and contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of subsurface processes.
Cloud-Based Seismic Processing
The migration of seismic processing to cloud-based platforms has streamlined data storage, accessibility, and processing capabilities. Cloud computing enables the rapid analysis of vast datasets, facilitating collaborative efforts among geoscientists, engineers, and decision-makers. This approach enhances the scalability and efficiency of seismic data processing workflows.
Time-Lapse Seismic Monitoring
Time-lapse or 4D seismic monitoring has become a standard practice in reservoir management. This technique involves repeated seismic surveys over time to monitor changes in subsurface conditions. By comparing multiple datasets, geoscientists gain insights into reservoir dynamics, fluid movements, and the effectiveness of enhanced oil recovery (EOR) methods.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
Advancements in seismic technology are not only improving exploration outcomes but also addressing environmental and cost considerations. Modern seismic acquisition techniques, such as low-impact and nodal seismic surveys, aim to minimize the environmental footprint of exploration activities. Additionally, efficient data processing and interpretation methods contribute to cost-effectiveness and sustainable exploration practices.
Paving the Way for Sustainable Exploration
The ongoing developments in seismic data acquisition, processing, and interpretation underscore a transformative period in the oil and gas industry. These advancements not only enhance the accuracy and efficiency of exploration but also contribute to sustainable and environmentally conscious practices. As technology continues to evolve, seismic data will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of energy exploration, enabling the industry to navigate complexities and unlock new opportunities beneath the Earth’s surface.